The cell cycle pt 1
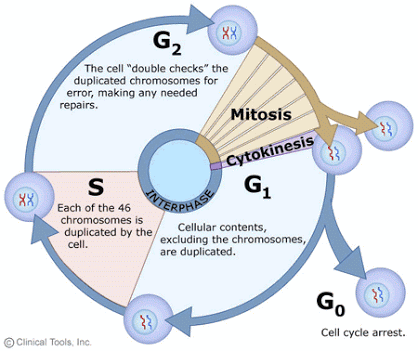
The cell cycle Actively dividing eukaryote cells pass through a series of stages known collectively as the cell cycle: two gap phases (G1 and G2); an S (for synthesis) phase, in which the genetic material is duplicated; and an M phase, in which mitosis partitions the genetic material and the cell divides. G1 phase Metabolic changes prepare the cell for division. At a certain point - the restriction point - the cell is committed to division and moves into the S phase. S phase. DNA synthesis replicates the genetic material. Each chromosome now consists of two sister chromatids. G2 phase Metabolic changes assemble the cytoplasmic materials necessary for mitosis and cytokinesis. M phase . A nuclear division (mitosis) followed by a cell division (cytokinesis). The period between mitotic divisions - that is, G1, S and G2 - is known as interphase. Mitosis Mitosis is a form of eukaryotic cell division that produces two daughter cells with the same genetic compo...